A cooling tower is a heat rejection device that removes excess heat from water-cooled industrial processes. It works by bringing water and air into contact, allowing a small portion of the water to evaporate and carry away heat. The cooled water is then recirculated back to the system.
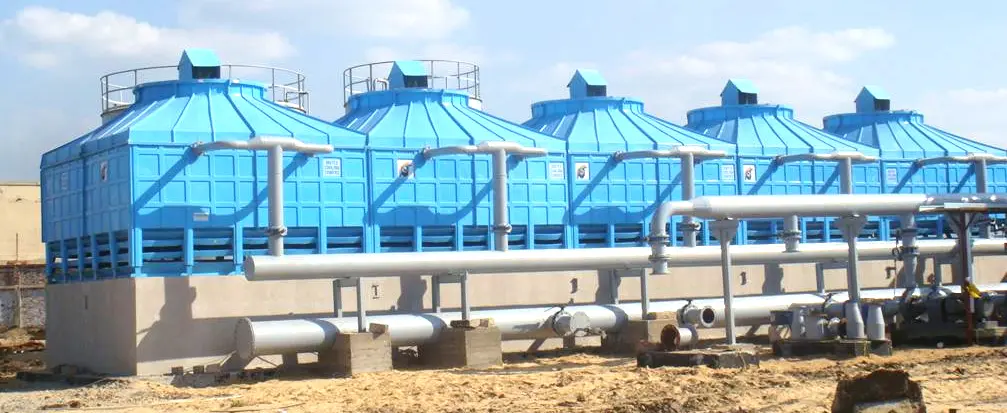

A cooling tower is a device that removes heat from water used in factories, power plants, and large air conditioning systems. It works through evaporative cooling, where warm water is exposed to air, and a small amount of it evaporates—cooling the rest of the water. The cooled water is then reused in the system to keep operations running smoothly.
Modern cooling towers are built with energy-saving designs and eco-friendly technology to reduce water use and carbon emissions. They play a key role in today’s sustainable industries by improving efficiency, lowering energy costs, and supporting greener cooling solutions.
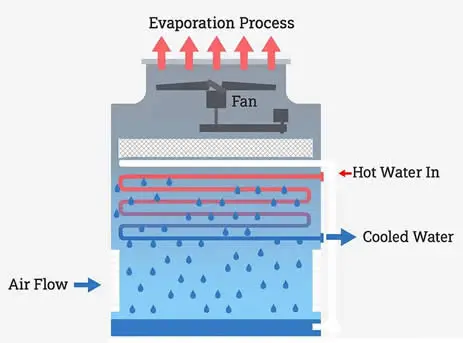
A cooling tower cools down water by using evaporation to remove heat. Warm water from industrial equipment or large HVAC systems is pumped to the top of the tower and spread over special materials called fills. These fills increase the water’s surface area, helping it mix better with air. As air moves through the tower—either by fans or natural flow—a small portion of the water evaporates.
This process takes away heat and cools the rest of the water. The cooled water is then collected at the bottom and sent back to the system for reuse, while warm, moist air is released into the atmosphere.
Today’s cooling towers are designed with energy-efficient fans, smart sensors, and water-saving technology. These upgrades help industries reduce energy use, lower operating costs, and support environment-friendly cooling. Modern materials and better designs also help minimize water loss and improve system reliability.

Cooling towers come in many designs, each made to suit different cooling needs, space limits, and working conditions. Below are the main types of cooling towers commonly used in industries, HVAC systems, and power plants.
A timber cooling tower uses high-quality treated wood for its structure. It is known for its strong design, durability, and resistance to harsh weather. These towers are often used in industries like steel plants, chemical units, and refineries where large-scale cooling is needed.
A dry cooling tower works without water evaporation. Instead, it uses air-cooled heat exchangers or fins to remove heat from the process water. This type is ideal for areas with limited water availability and helps save resources while maintaining efficient cooling.
A fanless cooling tower operates using natural air draft instead of mechanical fans. With no moving parts, it requires very low maintenance and runs quietly. It is suitable for smaller plants, hotels, and places where noise control and energy savings are priorities.
FRP cooling towers are lightweight, rust-free, and easy to install. Made from strong fiberglass-reinforced plastic, they are popular in HVAC systems, injection molding, and textile industries. Their compact size and long life make them ideal for both indoor and outdoor use.
An RCC cooling tower is built using heavy-duty reinforced concrete for long-term durability. It’s best for large industrial plants and power stations that need continuous cooling. These towers can handle high water loads and extreme weather conditions.
A skid mounted cooling tower is a portable and pre-assembled unit designed for quick installation and mobility. It’s often used for temporary cooling needs or where space is limited, such as construction sites, pilot plants, or rental cooling setups.
In a cross flow cooling tower, air moves horizontally across the falling water. This design allows for easy maintenance and stable performance. It’s widely used in HVAC systems, commercial buildings, and light industrial processes.
A counter flow cooling tower allows air to move upward while water flows downward. This opposite direction improves heat exchange efficiency and reduces drift loss. These towers are compact, energy-efficient, and suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Round cooling towers, also called bottle-shaped towers, are compact and designed for even air distribution. Their circular shape reduces wind resistance and improves cooling performance. They are commonly used in plastic molding, chemical plants, and power generation units.
A square shape cooling tower offers a modular design that allows easy capacity expansion. These towers provide uniform water distribution and are ideal for HVAC systems, cooling plants, and process industries.
An evaporative cooling tower removes heat by allowing a small portion of the water to evaporate into the air. This type is known for high efficiency and low operating cost, making it popular in manufacturing, refineries, and large buildings.
A natural draft cooling tower relies on natural airflow instead of mechanical fans to cool the water. These towers are massive, often used in thermal power plants, and built with concrete shells that create a chimney effect to move air naturally.
The best cooling tower depends on factors like cooling capacity, water availability, space, and energy use. Modern systems are designed to be energy-efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective, helping industries meet both operational and environmental goals.

Cooling towers offer several advantages for industries and large buildings by improving energy efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting sustainability. They help maintain stable process temperatures, protect equipment from overheating, and reduce the overall environmental footprint of cooling operations.
Cooling towers use the principle of evaporative cooling to remove heat effectively. By reducing the load on chillers and compressors, they lower overall energy consumption, leading to better system performance and efficiency.
Less energy use means lower electricity bills. In addition, maintaining ideal operating temperatures helps extend the lifespan of machinery, which reduces the need for frequent repairs or equipment replacement.
Stable cooling prevents overheating and wear, allowing machines to operate longer with fewer breakdowns. This ensures consistent performance and lowers long-term maintenance costs.
Efficient heat removal and reduced strain on equipment minimize downtime and maintenance expenses, helping industries run smoothly and profitably.
Modern cooling towers are designed to recycle and reuse water, cutting down on waste and promoting sustainable resource use. Advanced water management systems make them even more efficient and eco-friendly.
By improving energy efficiency, cooling towers help reduce greenhouse gas emissions that come from power generation and energy-intensive cooling methods. They provide a cleaner, more sustainable way to manage industrial heat.
Cooling towers quickly remove excess heat from industrial processes and HVAC systems, preventing equipment from overheating and ensuring continuous operation.
They help maintain steady temperatures, which is vital for the performance and safety of systems in manufacturing, power generation, and commercial buildings.
By keeping machinery within its optimal temperature range, cooling towers increase system reliability, reduce unplanned downtime, and improve productivity.
Cooling towers are used in a wide range of industries — from power plants and refineries to factories, data centers, and large commercial buildings — making them one of the most adaptable and valuable cooling solutions available.
With growing demand for energy-efficient and environmentally responsible technologies, cooling towers are more relevant than ever. Modern designs use smart controls, high-efficiency fans, and advanced materials to lower energy use, save water, and ensure reliable cooling for today’s industrial and HVAC applications.
Cooling towers are used across many industries to remove excess heat from equipment, process fluids, and air-conditioning systems. They help maintain efficient operations, prevent equipment failure, and improve energy performance in both industrial and commercial settings. From power plants to data centers, cooling towers play a key role in keeping systems stable and reliable.
Used in thermal, nuclear, and renewable power plants to cool steam from turbines and condensers. Cooling towers help maintain energy efficiency and stable electricity production.
Essential for refineries, petrochemical plants, and natural gas processing units. They remove heat from refining processes, compressors, and cooling lubricants.
Help manage the temperature of process fluids, reactors, and heat exchangers, ensuring safe and consistent chemical production.
Used to cool induction furnaces, rolling mills, and casting machines, improving metal quality and reducing wear on equipment.
Assist in cooling during pasteurization, chilling, and dairy processing operations. They also help control temperature for brewery and beverage production lines.
Maintain ideal temperatures for injection molds, extrusion, and blow molding machines, ensuring product consistency and faster production cycles.
Used to regulate temperature during dyeing, finishing, and fiber processing, preventing fabric damage and maintaining product quality.
Cooling towers are vital in air-conditioning systems for large buildings such as malls, hospitals, airports, and office complexes. They help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing energy consumption.
Used to remove heat produced by servers and electronic equipment, keeping them within safe operating limits and ensuring continuous, reliable performance.
Maintain precise temperature control for bioreactors, fermenters, and cleanroom environments, which is critical for quality and safety in drug manufacturing.
Used to cool equipment and process water in chemical, petroleum, and municipal treatment plants to ensure efficiency and compliance.
Cooling towers support industrial refrigeration systems by cooling and condensing refrigerants, helping maintain consistent cooling for storage and processing.